Clase 20: Regresiones¶
En esta clase revisaremos los conceptos econométricos de Mínimos Cuadrados Ordinarios (OLS por sus siglas en inglés) y Modelo Autorregresivo (AR por sus siglas en inglés).
Para esto vamos a utilizar la librería statsmodels: https://www.statsmodels.org/stable/install.html
Mínimos Cuadrados Ordinarios (Ordinary Least Squares)¶
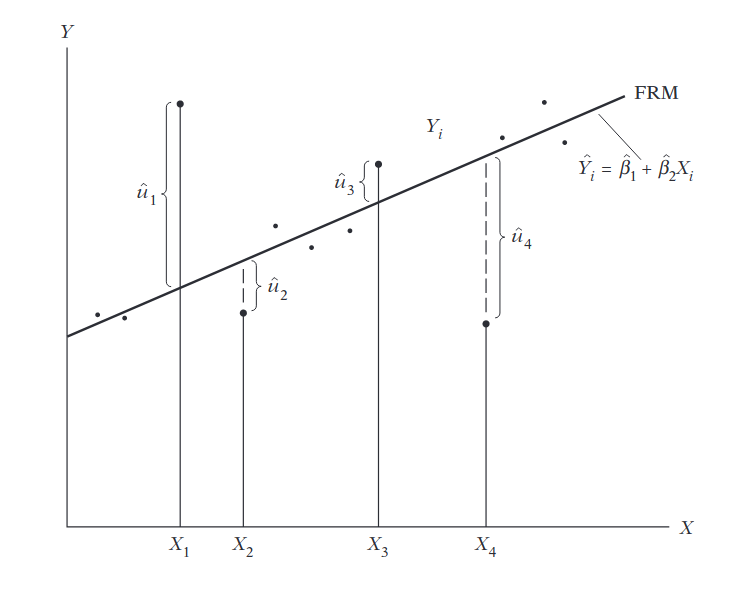
Buscamos estimar la Función de Regresión Poblacional (FRP), sin embargo esta no es observable directamente. Para esto vamos a utilizar una estimación que llamaremos la Función de Regresión Muestral (FRM):
FRP: \(Y_i = \beta_1 + \beta_2 X_i + \mu_i\)
FRM: \(Y_i = \hat{\beta}_1 + \hat{\beta}_2 X_i + \hat{\mu}_i = \hat{Y}_i - \hat{\mu}_i\), donde \(\hat{Y}_i\) es el valor estimado (media condicional) de \(Y_i\).
Entonces, en OLS vamos a minimizar el error \(\hat{\mu}_i = Y_i - \hat{Y_i}\) $\(\begin{align} \sum u_i^2 &= \sum (Y_i-\hat{Y}_i)^2 \\ &= \sum (Y_i - \hat{\beta}_1 - \hat{\beta}_2 X_i)^2 \end{align}\)$
from IPython.display import Image
Image("OLS1.png")
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.read_stata("/home/felix/Dropbox/Computational_Economics/Intro_python/Data_OLS_AR/Casen2020.dta");
/home/felix/miniconda3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/io/stata.py:1417: UnicodeWarning:
One or more strings in the dta file could not be decoded using utf-8, and
so the fallback encoding of latin-1 is being used. This can happen when a file
has been incorrectly encoded by Stata or some other software. You should verify
the string values returned are correct.
warnings.warn(msg, UnicodeWarning)
detalle_ingreso = df.ytrabajocor.describe()
detalle_ingreso
count 7.350900e+04
mean 5.783447e+05
std 1.264676e+06
min 4.000000e+00
25% 2.000000e+05
50% 3.681670e+05
75% 6.500000e+05
max 2.250000e+08
Name: ytrabajocor, dtype: float64
df2 = df[(df.ytrabajocor>0) & (df.ytrabajocor<10_000_000) & (df.ytrabajocor.notna())]
df2.ytrabajocor.describe()
count 7.345000e+04
mean 5.617230e+05
std 6.973099e+05
min 4.000000e+00
25% 2.000000e+05
50% 3.674275e+05
75% 6.500000e+05
max 9.850000e+06
Name: ytrabajocor, dtype: float64
plt.plot(df2.ytrabajocor, 'g')
plt.xlabel("Observación")
plt.ylabel('Ingreso del trabajo')
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-5-b7adf0787577> in <module>
----> 1 plt.plot(df2.ytrabajocor, 'g')
2 plt.xlabel("Observación")
3 plt.ylabel('Ingreso del trabajo')
NameError: name 'plt' is not defined
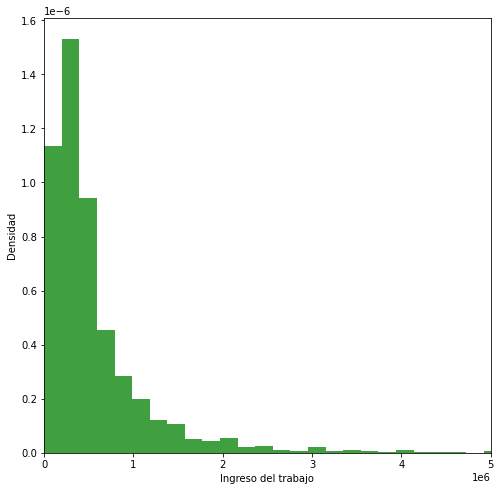
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.hist(df2.ytrabajocor, 50, density=True, facecolor='g', alpha=0.75)
plt.xlim([0, 5_000_000])
plt.xlabel('Ingreso del trabajo')
plt.ylabel('Densidad')
plt.show()
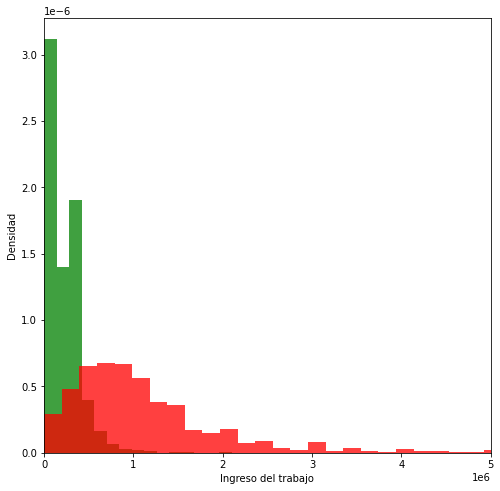
y_educ_bas = df2[["ytrabajocor", "educ"]][df2.educ=="Básica incompleta"].ytrabajocor
y_educ_uni = df2[["ytrabajocor", "educ"]][df2.educ=="Profesional completo"].ytrabajocor
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.hist(y_educ_bas, 50, density=True, facecolor='g', alpha=0.75)
plt.hist(y_educ_uni, 50, density=True, facecolor='r', alpha=0.75)
plt.xlim([0, 5_000_000])
plt.xlabel('Ingreso del trabajo')
plt.ylabel('Densidad')
plt.show()
Datos para la regresión
y = df2.ytrabajocor
X = df2.esc
X = sm.add_constant(X)
X.head()
| const | esc | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 12.0 |
| 3 | 1.0 | 15.0 |
| 4 | 1.0 | NaN |
| 5 | 1.0 | 16.0 |
| 7 | 1.0 | 15.0 |
#Hay que limpiar los NaN en variable exógena
df3 = df[(df.ytrabajocor>0) & (df.ytrabajocor<10_000_000) & (df.ytrabajocor.notna()) & (df.esc.notna())]
y = df3.ytrabajocor
X = df3.esc
X = sm.add_constant(X)
X.head()
| const | esc | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 12.0 |
| 3 | 1.0 | 15.0 |
| 5 | 1.0 | 16.0 |
| 7 | 1.0 | 15.0 |
| 11 | 1.0 | 14.0 |
y = df3.ytrabajocor
X = df3.esc
X = sm.add_constant(X)
X.head()
import statsmodels.api as sm
model = sm.OLS(y, X)
results = model.fit()
print(results.summary())
OLS Regression Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: ytrabajocor R-squared: 0.183
Model: OLS Adj. R-squared: 0.183
Method: Least Squares F-statistic: 1.601e+04
Date: Mon, 26 Jul 2021 Prob (F-statistic): 0.00
Time: 22:21:34 Log-Likelihood: -1.0554e+06
No. Observations: 71466 AIC: 2.111e+06
Df Residuals: 71464 BIC: 2.111e+06
Df Model: 1
Covariance Type: nonrobust
==============================================================================
coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const -3.694e+05 7751.498 -47.662 0.000 -3.85e+05 -3.54e+05
esc 7.572e+04 598.451 126.532 0.000 7.45e+04 7.69e+04
==============================================================================
Omnibus: 64620.243 Durbin-Watson: 1.630
Prob(Omnibus): 0.000 Jarque-Bera (JB): 3238679.663
Skew: 4.257 Prob(JB): 0.00
Kurtosis: 34.861 Cond. No. 43.0
==============================================================================
Notes:
[1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified.
No. Observations: número de observaciones ocupadas en la regresión.
R-squared: El \(R^2\) es la proporción de la varianza en la variable dependiente que puede ser predicha por las variables independientes. En este caso un 18% de la varianza es explicada por las variables independientes.
Adj R-squared (\(R^2\) ajustado): el \(R^2\) se ajusta para penalizar que se agreguen regresores extraños.
F-statistic (F(Z,)): Es la razón entre el error cuadrático medio del modelo y el error cuadrático medio de los residuos. Nos sirve para determinar la importancia general del modelo.
Criterios de información (AIC y BIC): nos sirven para ver el trade-off entre complejidad del modelo y bondad de ajuste de este.
Image("OLS3.png")

En las filas están las variables con las que regresionamos: constante y educación. En las columnas tenemos:
El coeficiente de las variables independientes y la constante. Acá estamos estimando los \(\beta_i\): \(Y_i = \hat{\beta}_1 + \hat{\beta}_2 X_i + \hat{\mu}_i\)
std err: error estándar asociado a los coeficientes.
t: estadístico t usado para testear la significancia de los coeficientes.
\(P>|t|\): p-value de dos colas usado para testear hipótesis nula de que el coeficiente es cero (\(\alpha=0.05\)).
[0.025 - 0.975]: intervalo de confianza de coeficiente con \(\alpha=0.05\).
#df.loc[df['column name'] condition, 'new column name'] = 'value if condition is met'
df3.loc[df3.sexo=="Hombre", "sexo2"] = 0
df3.loc[df3.sexo=="Mujer", "sexo2"] = 1
/home/felix/miniconda3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/indexing.py:1599: SettingWithCopyWarning:
A value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.
Try using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
self.obj[key] = infer_fill_value(value)
/home/felix/miniconda3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pandas/core/indexing.py:1720: SettingWithCopyWarning:
A value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.
Try using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
self._setitem_single_column(loc, value, pi)
y = df3.ytrabajocor
X = df3[["esc", "edad", "sexo2"]]
X = sm.add_constant(X)
X.head()
| const | esc | edad | sexo2 | esc2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 12.0 | 34 | 1.0 | 144.0 |
| 3 | 1.0 | 15.0 | 45 | 0.0 | 225.0 |
| 5 | 1.0 | 16.0 | 57 | 0.0 | 256.0 |
| 7 | 1.0 | 15.0 | 56 | 1.0 | 225.0 |
| 11 | 1.0 | 14.0 | 54 | 1.0 | 196.0 |
df3['exp'] = df3.edad-df3.esc
df3['exp2'] = df3.exp**2
df3['exp_sexo'] = df3.exp*df3.sexo2
y = np.log(df3.ytrabajocor)
X = df3[["esc", "exp", "exp2", "sexo2", "exp_sexo"]]
X = sm.add_constant(X)
X.head()
<ipython-input-18-79fecfcd28f3>:1: SettingWithCopyWarning:
A value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.
Try using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df3['exp'] = df3.edad-df3.esc
<ipython-input-18-79fecfcd28f3>:2: SettingWithCopyWarning:
A value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.
Try using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df3['exp2'] = df3.exp**2
<ipython-input-18-79fecfcd28f3>:3: SettingWithCopyWarning:
A value is trying to be set on a copy of a slice from a DataFrame.
Try using .loc[row_indexer,col_indexer] = value instead
See the caveats in the documentation: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/indexing.html#returning-a-view-versus-a-copy
df3['exp_sexo'] = df3.exp*df3.sexo2
| const | esc | exp | exp2 | sexo2 | exp_sexo | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 12.0 | 22.0 | 484.0 | 1.0 | 22.0 |
| 3 | 1.0 | 15.0 | 30.0 | 900.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 5 | 1.0 | 16.0 | 41.0 | 1681.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 7 | 1.0 | 15.0 | 41.0 | 1681.0 | 1.0 | 41.0 |
| 11 | 1.0 | 14.0 | 40.0 | 1600.0 | 1.0 | 40.0 |
model = sm.OLS(y, X)
results = model.fit()
print(results.summary())
OLS Regression Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: ytrabajocor R-squared: 0.265
Model: OLS Adj. R-squared: 0.265
Method: Least Squares F-statistic: 5151.
Date: Tue, 26 Oct 2021 Prob (F-statistic): 0.00
Time: 11:08:12 Log-Likelihood: -1.1887e+05
No. Observations: 71466 AIC: 2.378e+05
Df Residuals: 71460 BIC: 2.378e+05
Df Model: 5
Covariance Type: nonrobust
==============================================================================
coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const 9.7314 0.030 326.486 0.000 9.673 9.790
esc 0.1522 0.002 100.943 0.000 0.149 0.155
exp 0.0820 0.001 71.234 0.000 0.080 0.084
exp2 -0.0011 1.56e-05 -68.238 0.000 -0.001 -0.001
sexo2 -0.1503 0.021 -7.152 0.000 -0.191 -0.109
exp_sexo -0.0136 0.001 -23.036 0.000 -0.015 -0.012
==============================================================================
Omnibus: 31679.342 Durbin-Watson: 1.650
Prob(Omnibus): 0.000 Jarque-Bera (JB): 197590.127
Skew: -2.052 Prob(JB): 0.00
Kurtosis: 10.037 Cond. No. 1.12e+04
==============================================================================
Notes:
[1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified.
[2] The condition number is large, 1.12e+04. This might indicate that there are
strong multicollinearity or other numerical problems.
y = np.log(df3.ytrabajocor)
X = df3[["esc", "edad", "sexo2"]]
X = sm.add_constant(X)
X.head()
| const | esc | edad | sexo2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | 12.0 | 34 | 1.0 |
| 3 | 1.0 | 15.0 | 45 | 0.0 |
| 5 | 1.0 | 16.0 | 57 | 0.0 |
| 7 | 1.0 | 15.0 | 56 | 1.0 |
| 11 | 1.0 | 14.0 | 54 | 1.0 |
model = sm.OLS(y, X)
results = model.fit()
print(results.summary())
OLS Regression Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: ytrabajocor R-squared: 0.212
Model: OLS Adj. R-squared: 0.212
Method: Least Squares F-statistic: 6423.
Date: Mon, 26 Jul 2021 Prob (F-statistic): 0.00
Time: 23:38:58 Log-Likelihood: -1.2134e+05
No. Observations: 71466 AIC: 2.427e+05
Df Residuals: 71462 BIC: 2.427e+05
Df Model: 3
Covariance Type: nonrobust
==============================================================================
coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const 10.5982 0.028 380.688 0.000 10.544 10.653
esc 0.1696 0.001 124.958 0.000 0.167 0.172
edad 0.0039 0.000 10.597 0.000 0.003 0.005
sexo2 -0.5787 0.010 -58.179 0.000 -0.598 -0.559
==============================================================================
Omnibus: 32963.117 Durbin-Watson: 1.642
Prob(Omnibus): 0.000 Jarque-Bera (JB): 198868.520
Skew: -2.170 Prob(JB): 0.00
Kurtosis: 9.925 Cond. No. 269.
==============================================================================
Notes:
[1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified.
print('Parámetros: ', results.params)
print('Error estandar: ', results.bse)
print('Valores predichos: ', results.predict())
Parámetros: const 10.598153
esc 0.169602
edad 0.003898
sexo2 -0.578690
dtype: float64
Error estandar: const 0.027839
esc 0.001357
edad 0.000368
sexo2 0.009947
dtype: float64
Valores predichos: [12.18721169 13.31758263 13.5339568 ... 12.31583427 10.77744552
11.22416493]
Comparar resultados predichos
from statsmodels.sandbox.regression.predstd import wls_prediction_std
prstd, iv_l, iv_u = wls_prediction_std(results)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,6))
ax.plot(X.esc, y, 'o', label="data")
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x7f4486a0d9d0>]
Para ver ejemplos de gráficos en modelos de regresión pueden utilizar https://www.statsmodels.org/stable/examples/notebooks/generated/regression_plots.html
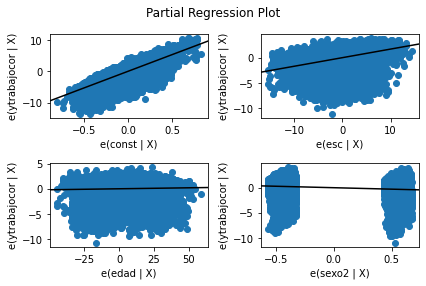
Por ejemplo, una visualización de las regresiones parciales se puede obtener mediante plot_partregress_grid. Esto muestra la relación entre la respuesta y la variable explicativa después de eliminar el efecto de todas las otras variables exógenas.
#Para ver gráficos de las regresiones parciales (regresionar la variable dependiente c/r a una variable condicional en el resto de las variables exógenas)
fig = sm.graphics.plot_partregress_grid(results)
fig.tight_layout(pad=1.0)
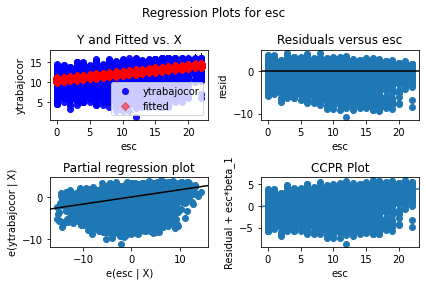
Para ver información de la regresión con respecto a una variable en específico podemos ocupar plot_regress_exog. Acá tenemos
Fitted plot
Residuo
Regresión parcial
Component-Component plus Residual (CCPR) plot: nos sirve para ver la relación entre uan variable independiente particular y la variable de respuesta, dado que otras variables indpendientes también están presentes en el modelo: \(Res+\hat{\beta}_iX_i\) versus \(X_i\)
fig = sm.graphics.plot_regress_exog(results, "esc")
fig.tight_layout(pad=1.0)
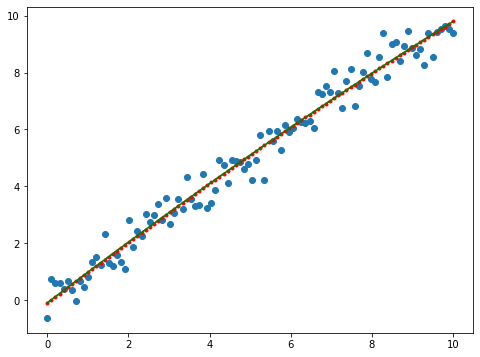
Ejemplo caso con menos ruido: ejemplo de juguete
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = x + 0.5 * np.random.normal(size=len(x))
plt.plot(x,y)
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x7f44946253d0>]
X = np.column_stack((x, x**2))
X = sm.add_constant(X)
res = sm.OLS(y, X).fit()
print(res.summary())
OLS Regression Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: y R-squared: 0.974
Model: OLS Adj. R-squared: 0.973
Method: Least Squares F-statistic: 1807.
Date: Mon, 26 Jul 2021 Prob (F-statistic): 1.73e-77
Time: 23:31:42 Log-Likelihood: -66.869
No. Observations: 100 AIC: 139.7
Df Residuals: 97 BIC: 147.6
Df Model: 2
Covariance Type: nonrobust
==============================================================================
coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const -0.0904 0.141 -0.641 0.523 -0.370 0.189
x1 1.0865 0.065 16.670 0.000 0.957 1.216
x2 -0.0098 0.006 -1.557 0.123 -0.022 0.003
==============================================================================
Omnibus: 0.781 Durbin-Watson: 2.028
Prob(Omnibus): 0.677 Jarque-Bera (JB): 0.817
Skew: -0.006 Prob(JB): 0.665
Kurtosis: 2.557 Cond. No. 144.
==============================================================================
Notes:
[1] Standard Errors assume that the covariance matrix of the errors is correctly specified.
# y_hat = res.params[0] + results.params[1] * x + results.params[1] * x**2
res.params[2]
-0.009817635455210468
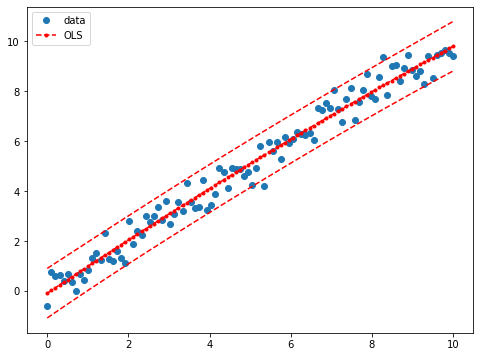
prstd, iv_l, iv_u = wls_prediction_std(res)
#Retorno:
#-standard error of prediction same length as rows of exog
#-lower und upper confidence bounds
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,6))
ax.plot(x, y, 'o', label="data")
ax.plot(x, res.fittedvalues, 'r--.', label="OLS")
ax.plot(x, iv_u, 'r--')
ax.plot(x, iv_l, 'r--')
ax.legend(loc='best');
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8,6))
y_hat = res.params[0] + res.params[1] * x + res.params[2] * x**2
ax.plot(x, y, 'o', label="data")
ax.plot(x, res.fittedvalues, 'r--.', label="OLS")
ax.plot(x, y_hat, 'g', label="OLS")
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x7f4494171280>]
Modelo Autorregresivo (AR)¶
Podemos estimar un modelo del tipo \(Y_t = \beta_0 + \beta_1 Y_{t-1} + \mu_t\)
En python podemos utilizar AutoReg: https://www.statsmodels.org/stable/examples/notebooks/generated/autoregressions.html
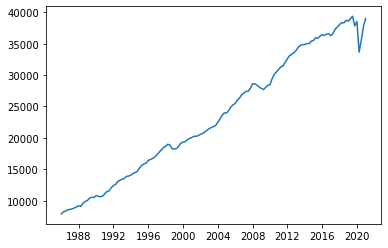
df = pd.read_excel("/home/felix/Dropbox/Computational_Economics/Intro_python/Data_OLS_AR/pib.xlsx")
df.dtypes
df.head()
| Periodo | PIB | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1986-01-01 | 7899.666547 |
| 1 | 1986-04-01 | 8220.056395 |
| 2 | 1986-07-01 | 8355.276664 |
| 3 | 1986-10-01 | 8555.927503 |
| 4 | 1987-01-01 | 8626.993492 |
plt.plot(df.Periodo, df.PIB);
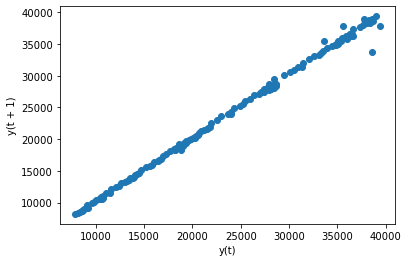
from pandas.plotting import lag_plot
lag_plot(df.PIB)
<AxesSubplot:xlabel='y(t)', ylabel='y(t + 1)'>
from statsmodels.tsa.ar_model import AutoReg, ar_select_order
from statsmodels.tsa.api import acf, pacf, graphics
mod = AutoReg(df.PIB, 1, old_names=False)
res = mod.fit()
print(res.summary())
AutoReg Model Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: PIB No. Observations: 141
Model: AutoReg(1) Log Likelihood -1085.062
Method: Conditional MLE S.D. of innovations 562.000
Date: Tue, 27 Jul 2021 AIC 12.706
Time: 08:19:50 BIC 12.769
Sample: 1 HQIC 12.731
141
==============================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const 257.5324 123.602 2.084 0.037 15.278 499.787
PIB.L1 0.9985 0.005 203.603 0.000 0.989 1.008
Roots
=============================================================================
Real Imaginary Modulus Frequency
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
AR.1 1.0015 +0.0000j 1.0015 0.0000
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Podemos actualizar el modelo a \(Y_t = \beta_0 + \beta_1 Y_{t-1} + \beta_2 Y_{t-2} + \beta_3 Y_{t-3} + \beta_4 Y_{t-4} + \beta_5 Y_{t-5} + \mu_t\)
mod = AutoReg(df.PIB, 5, old_names=False)
res = mod.fit()
print(res.summary())
AutoReg Model Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: PIB No. Observations: 141
Model: AutoReg(5) Log Likelihood -1047.475
Method: Conditional MLE S.D. of innovations 535.438
Date: Tue, 27 Jul 2021 AIC 12.669
Time: 08:21:12 BIC 12.819
Sample: 5 HQIC 12.730
141
==============================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const 423.0718 133.111 3.178 0.001 162.179 683.965
PIB.L1 0.8942 0.083 10.802 0.000 0.732 1.056
PIB.L2 0.2591 0.123 2.105 0.035 0.018 0.500
PIB.L3 -0.3180 0.120 -2.658 0.008 -0.553 -0.083
PIB.L4 -0.5179 0.223 -2.323 0.020 -0.955 -0.081
PIB.L5 0.6816 0.195 3.488 0.000 0.299 1.065
Roots
=============================================================================
Real Imaginary Modulus Frequency
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
AR.1 -0.8762 -0.6971j 1.1197 -0.3930
AR.2 -0.8762 +0.6971j 1.1197 0.3930
AR.3 0.7558 -0.7735j 1.0814 -0.1268
AR.4 0.7558 +0.7735j 1.0814 0.1268
AR.5 1.0006 -0.0000j 1.0006 -0.0000
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
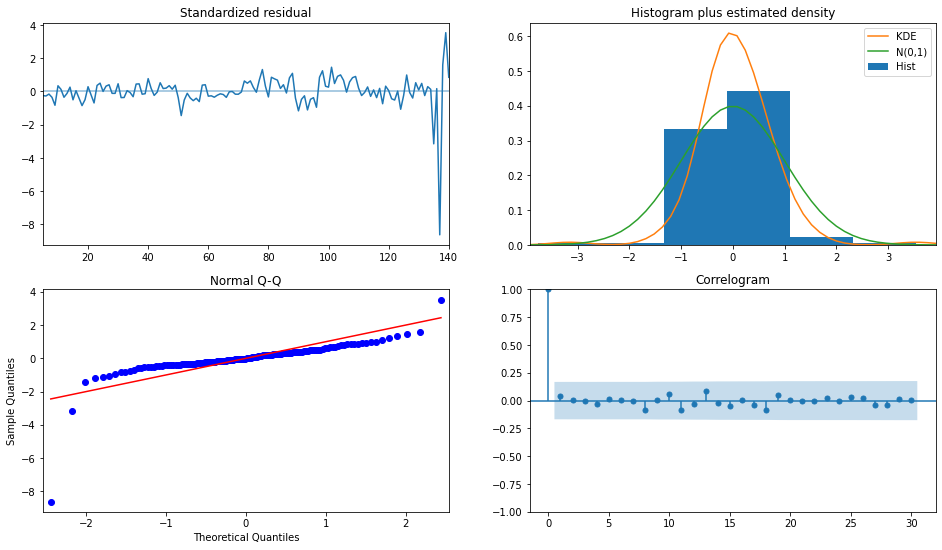
Para un resumen de la visualización de los residuos estandarizados podemos ocupar plot_diagnostics
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16,9))
fig = res.plot_diagnostics(fig=fig, lags=30)
#Standarized residual:
#-residuo: Valor observado - valor predicho
#-standarized residual: residuo normalizado por el error estandar del modelo (RSE)
#Histogram plus: estima la distribución de los residuos estandarizados. Nos muestra la distribución normal (línea verde) como punto de comparación.
#Normal Q-Q : muestra si el residuo está distribuido normalmente. Lo que se espera es que los puntos se encuentren sobre la línea roja o cercanos a ella.
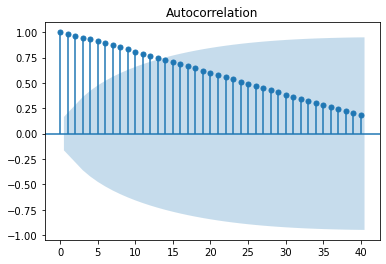
#Correlograma: nos muestra un gráfico de autocorrelaciones
Autocorrelaciones: https://www.statsmodels.org/stable/generated/statsmodels.graphics.tsaplots.plot_acf.html
sm.graphics.tsa.plot_acf(df.PIB, lags=40)
plt.show()
Actividad¶
Estime la ecuación de mincer: \(Ingreso_i = \beta_0 + \beta_1 esc_i + \beta_2 exp_i + \beta_3 exp_i^2 + \beta_4 sexo_i + \mu_i\) donde :
ingreso: log(ingreso del trabajo)
esc: escolaridad
exp: experiencia = edad - escolaridad
exp2: expediencia al cuadrado
sexo: variable dicotómica si es hombre (0) o mujer (1).
Estime un modelo AR del tipo \(\Delta y_t = \Delta y_{t-1}\) donde:
\(y_t\) es el PIB trimestral en el periodo t.
\(\Delta y_t\) es la variación del PIB trimestral en el periodo t.
\(\Delta y_{t-1}\) es la variación del PIB trimestral en el periodo t-1.
